How to Set Up Schema Markup for Subscription & Paywalled Content Using Schema Package
This guide explains how to configure subscription and paywalled content structured data using the Schema Package plugin, based on Google’s official guidelines for paywalled content.
Reference (Google Docs):
https://developers.google.com/search/docs/appearance/structured-data/paywalled-content
📌 What Is Paywalled / Subscription Content Schema?
Paywalled content schema tells Google:
- Whether content is free or locked
- Which parts of the page are restricted
- That users may need to subscribe or log in
This helps Google:
- Understand access restrictions
- Avoid ranking issues due to hidden content
- Display correct search appearance
🧠 How Schema Package Implements Paywalled Content
Schema Package supports paywalled markup in two ways:
- Apply Paywall Schema Automatically (Global Setup)
- Post-Specific Setup (Schema Package Generator)
Both methods generate Google‑compliant structured data automatically.
🔹 Method 1 — Apply Paywall Schema Automatically (Global Setup)
Step 1 — Configure Schema Markup Using Reference documentation
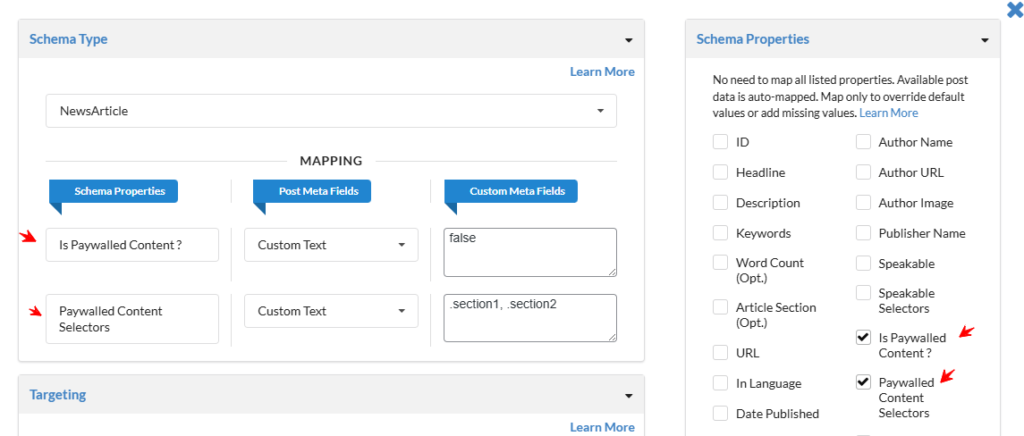
Step 2 — Map Paywalled Properties
After adding schema, map these two properties:
✅ Property 1 — Is Paywalled Content?
- Field Type: Custom Text
- Value:
false
✅ Property 2 — Paywalled Content Selectors
- Field Type: Custom Text
- Value (Comma‑Separated CSS Selectors): eg : .section1, .section2
This tells Google which page elements contain restricted content.
🔹 Method 2 — Post-Specific Setup (Schema Package Generator)
Step 1 — Configure Schema Markup Using Reference documentation
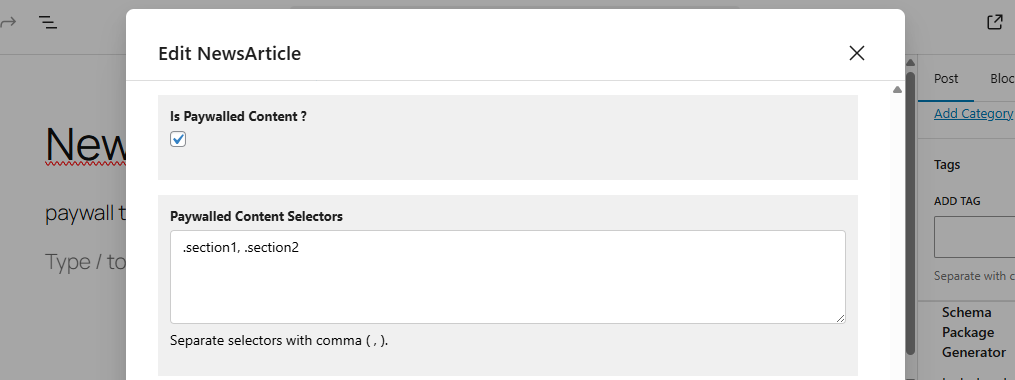
Step 2 — Enable Paywalled Content
Toggle the checkbox:
✔ Is Paywalled Content?
Step 3 — Add Paywalled Content Selectors
Paste your CSS selectors inside the textarea: (eg: .section1, .section2)
🔹 Example HTML Structure (For Understanding Selectors)
Below is a simplified example showing how Schema Package detects paywalled sections.
<html>
<head>
<title>Article headline</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "NewsArticle",
"headline": "Article headline",
"image": "https://example.org/thumbnail1.jpg",
"datePublished": "2025-02-05T08:00:00+08:00",
"dateModified": "2025-02-05T09:20:00+08:00",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "John Doe",
"url": "https://example.com/profile/johndoe123"
},
"description": "A most wonderful article",
"isAccessibleForFree": false,
"hasPart": {
"@type": "WebPageElement",
"isAccessibleForFree": false,
"cssSelector": ".paywall"
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="non-paywall">
Non-Paywalled Content
</div>
<div class="section1">
Paywalled Content
</div>
<div class="section2">
Paywalled Content
</div>
</body>
</html>
🔹 Generated Structured Data Output (Concept)
Schema Package automatically outputs:
"isAccessibleForFree": false,
"hasPart": [
{
"@type": "WebPageElement",
"isAccessibleForFree": false,
"cssSelector": ".section1"
},
{
"@type": "WebPageElement",
"isAccessibleForFree": false,
"cssSelector": ".section2"
}
]
This matches Google’s official structured data format.
🔹 Best Practices
✅ Use accurate CSS selectors
✅ Avoid marking free content as locked
✅ Ensure locked content is actually hidden from users
✅ Test schema in Google Rich Results Test
🔹 Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Adding selectors that don’t exist in HTML
❌ Marking all content paywalled when previews exist
❌ Using unsupported schema types
❌ Blocking Googlebot from crawling content
🔹 Final Notes
Schema Package ensures your subscription and paywalled content follows Google Search structured data policies, helping protect rankings and eligibility.
Note: This setup requires identifying CSS selector classes from the post/page HTML source, which may involve some technical knowledge. If you face any difficulties, feel free to reach out, our team will gladly help you.